It’s almost impossible to eat a healthy diet without using a computer. It would be a gigantic job to create a diet that contains the exact amount of calories, proteins, amino acids, vitamins, minerals,… by only using a sheet of paper and books. The computer program that I use is a free downloadable program called CRON-O-METER.
You can download it from here:
http://spaz.ca/cronometer/
This program calculates the amount of calories, fibers, water, alcohol, caffeine, starch, ash, sugars, vitamins, minerals, amino acids and fats. You are able to create a log which the values of blood glucose, weight, body temperature, systolic BP, diastolic BP and resting heart rate. You can create new foods or adjust existing ones.
Of course there are some other programs that you could use.
What I do is making a diet in the evening for the following day. That is much easier if you have to go to school or go to work.
Two meals a day versus more smaller meals a day.
Some people advise to eat only 2 meals a day. Let’s say one at 12.00h (12am) and one at 18.00h (6pm). By doing that the time between your meal at 18.00h and that at 12.00h is 18 hours. So they say that in that 18 hours your insulin levels are low and that is beneficial. People who support the more smaller meals a day say that by eating a smaller meal your insulin levels don’t change dramatically from very low to high. Of course these smaller meals must be made of foods on which your body only releases a small amount of insulin.
Sunday 2 September 2007
Sunday 26 August 2007
Extracellular cross links
All the proteins in our cells are replaced quite regularly because they get damaged. But some of the proteins outside our cells aren’t replaced or only very slowly. The working is often very simple, so a minor change isn’t that serious. But after a while it can cause problems. Mostly they have a biophysical function like give a tissue elasticity (for example the artery wall) or high tensile strength like the ligaments or transparency like the lens of the eye. A good example of one of the problems which extracellular cross links is the case of the artery wall which becomes more rigid and leads to high blood pressure. When two proteins in our artery wall bond together (cross-linking) then they loose there ability to slide across or along each other. Luckily, a lot of these structure have very unusual chemical structures, not found in proteins our other molecules that the body makes on purpose. This means that it’s possible to make molecules that break these cross links without reacting which other molecules that your body needs. One of these cross-links breakers is ALT-711, today known as alagebrium chloride. But there are cross-links that alagebrium chloride can’t break, so we need to develop some other cross-link breakers too. A problem is that some molecules are too stable to be broken down by a non-toxic small molecule. Maybe you will ask yourself: “why can toxic molecules break it while non toxic can’t”. Well this is because some toxic molecules our very reactive and will not only beak the cross-link but also the rest of the molecules inside your body. The solution for this problem can be the creation of enzymes that can break these cross-links or other molecules that bound to stable molecules but inactivate themselves when they are bounded. Alagebrium chloride can also beak down glycolysation end-products (A.G.E.s).
Saturday 25 August 2007
Junk inside cells
Cells are constantly breaking down big molecules into smaller ones. One of the reasons why they have to do it is because the molecule doesn’t work like it should do. But why does these molecules loose there function? Well, because there have been chemically altered. Sometimes a molecule is created for which your body doesn’t have the machinery to break it down. These big molecules accumulate in your cells. Just like polyethylene on a landfill, no single micro-organism is capable of breaking down polyethylene, so it stays there forever. These molecules accumulate in the lysosomes. The lysosomes are organelles that contain digestive enzymes. The function of a lysosome is to break down molecules and even hole parts of the cell that are to damaged to work (autophagy). When cells dived the junk is divided into two cells, so these cells have some kind of protection against to much junk. But cells that doesn’t divide are gradually filled which junk. These cells include nerve cells (motor neurons), heart cells, white blood cells trapped within the artery wall and some cells in the eye. This can lead to macular degradation (blindness), arthrosclerosis (heart attacks and strokes), some neurodegenerative diseases. A good example of what happen if junk is stored in lysosomes is Tay-Sachs disease. In this disease people the enzyme hexosaminidase A needed to break down gangliosides isn’t working properly. Scientists are developing enzymes that could break down these resistant molecules.

1. Nucleolus
2. Nucleus
3. Ribosome
4. Vesicle
5. Rough endoplasmic reticulum
6. Golgi apparatus
7. Cytoskeleton
8. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
9. Mitochondrion
10. Vacuole
11. Cytoplasm
12. Lysosome
13. Centriole
Friday 24 August 2007
What can you do to support the anti aging socienty
When people become old they get medical problems like osteoporoses, diabetes type II, Alzheimer, dementia,… They have sometimes problems to walk. If you don’t want to become like this than is anti aging something for you. Than you could ask yourself: “What can I do to support the anti aging society?”. Well, I will give here some things you could do:
- Tell your family and friends about this
- Write a site or blog about anti aging
- Become a member from imminst, this costs 50 dollar a year and they use your money to make films, write books,… about anti aging.
- Sign the petition on http://www.coalitiontoextendlife.org/news.php#petition
- Make a movie about anti aging and place it on youtube
- Donate to the Methuselah Foundation http://www.mprize.org/donate
It’s critically important for us to inform as many people as possible about anti aging. For getting funds from the government we need to have a lot of people who support us. Don’t forget every day that we wait, people will die unnecessary.
- Tell your family and friends about this
- Write a site or blog about anti aging
- Become a member from imminst, this costs 50 dollar a year and they use your money to make films, write books,… about anti aging.
- Sign the petition on http://www.coalitiontoextendlife.org/news.php#petition
- Make a movie about anti aging and place it on youtube
- Donate to the Methuselah Foundation http://www.mprize.org/donate
It’s critically important for us to inform as many people as possible about anti aging. For getting funds from the government we need to have a lot of people who support us. Don’t forget every day that we wait, people will die unnecessary.

Cell los and atrophy
Cells can’t live forever, except for cancer cells (these live forever if they are preserved in the right conditions). The number of times that a cell can divide is called the Hayflick limit. For a human cell this limit is about 52 times. But how does a cell know how many times that she’s already divided? Well the answer is because a cell uses a mechanism to count this. This mechanism are the telomeres. The telomeres are pieces of DNA on the end of the DNA molecule that doesn’t code for the production of proteins. When the cell divides the DNA is replicated and the telomere becomes shorter. When there isn’t any more telomere, the vital DNA would become shorter and the cell wouldn’t be able to produce the right kind of proteins. So the cell commits suicide. Cancer cells produce an enzyme called telomerase that lengthens the telomeres and by doing so prevent the cell from dying. Now researchers search drugs that inhibit telomerase and this makes cancer cells mortal. A good example of cancer cells' immortality is HeLa cells, which were originally removed from the cervical cancer of Henrietta Lacks in 1951 and are still used in laboratories as a model cell line. They are indeed immortal - daily production of HeLa cells is estimated at several tons even up to this day - all from the few cells taken from Ms. Lacks' tumor.
Mutations of the mitochondrial DNA
Research has shown that mitochondrial DNA has a fast mutation speed. That’s why these mutations accelerate the aging process more than mutations of the nuclear DNA. The mitochondrion’s are the energy factories of our bodies. Free radials are a by-product of the energy production. When you take antioxidants to slow down the aging process you have to be sure that you don’t forget your mitochondria. For example, lipoic acid is one of the few antioxidant that are capable of going inside the mitochondria of the brain and protect them. Antioxidants that are capable of going inside mitochondria are: lipoic acid, melatonin, MitoQ, MitoVit E,… As far as I know you cannot buy these last two (MitoQ and MitoVit E) for supplement purpose. You can only buy the to do research. There are not many safety studies done, that’s why I advise not to take them. If you take to much your ATP will be disrupt and you will die. But the other two (lipoic acid and melatonin) are perfectly safe to take.

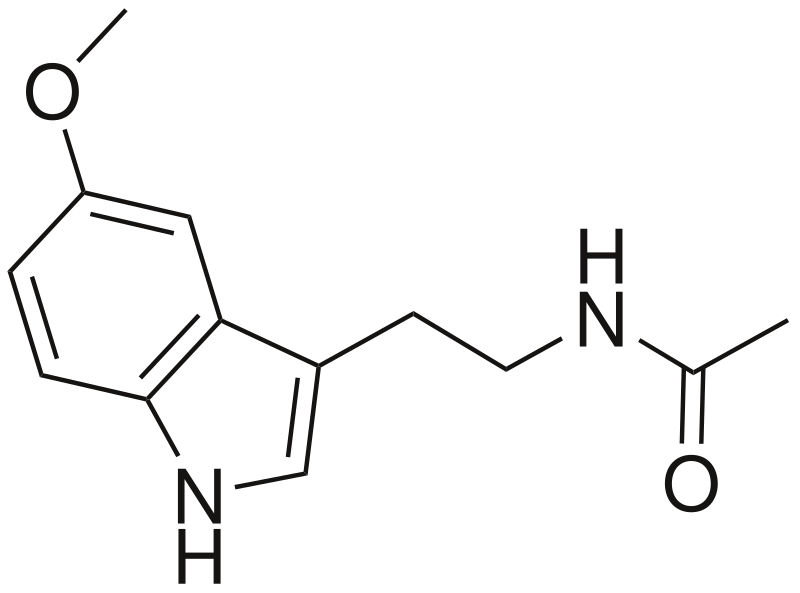
Melatonin
 Lipoic acid
Lipoic acid
Ending Aging: The Rejuvenation Breakthroughs That Could Reverse Human Aging in Our Lifetime

This book is wrote by Dr. Aubrey de Grey who works in the department of genetics at the university of Cambrige. He's one of the leading investigators of human aging. The book will be released on 4 September 2007. I'm looking forward to reed it.
You can pre-order it by amazon:
http://www.amazon.com/Ending-Aging-Rejuvenation-Breakthroughs-Lifetime/dp/0312367066
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
